The Hidden Costs of Subscription Services: How to Audit and Cut Monthly Expenses
Anúncios
In today’s digital economy, subscription services have become an integral part of everyday life. From streaming platforms and software tools to meal kits and fitness apps, subscriptions provide convenience and continuous access to myriad products and services. However, the cumulative cost of multiple subscriptions often goes unnoticed, quietly draining consumers’ wallets month after month. According to a 2023 report by West Monroe Partners, the average American spends approximately $237 per month on subscription services, with nearly 70% of those individuals unaware of how much they actually pay monthly.
This phenomenon of “subscription creep” often leads to wasted expenditures on unused or underutilized services. Identifying and managing these hidden expenses requires a strategic approach to personal finance—a subscription audit—that enables users to optimize spending and maintain control over recurring charges. This article explores the underlying costs associated with subscription services, the techniques for auditing these expenses, and practical steps to trim monthly bills effectively.

Anúncios
An organized personal finance scene showing a person auditing multiple subscription services on a laptop and smartphone, surrounded by bills, charts, and subscription logos like Netflix, Spotify, and Adobe, illustrating the concept of “subscription audit” and managing hidden costs.
Understanding the Subscription Economy: More Than Meets the Eye
Anúncios
Subscription services have transformed the traditional consumer landscape by shifting from one-time payments to ongoing monthly or annual fees. This model benefits businesses through predictable revenue streams and fosters customer loyalty, while consumers enjoy uninterrupted access and frequent updates. However, the ease of subscription sign-up masks the potential for accumulating excessive charges.
A study conducted by McKinsey in 2022 reveals that 55% of consumers are subscribed to more than four subscription services, and 22% fail to cancel at least one subscription in the past year they did not use. Hidden fees, tier upgrades, add-ons, and auto-renewals often contribute to escalating costs. For example, Spotify’s premium family plan costs $15.99 a month, but many users add multiple individual accounts or associated services such as podcasts or audiobooks, leading to an overall higher expense than initially expected.
The hidden costs also include impacted credit scores and financial stress from unnoticed withdrawals. Many consumers sign up for free trials and forget to cancel, resulting in automatic payments. In some cases, cancellation processes are intentionally complicated, leading to continued charges. Therefore, awareness and vigilance become crucial to managing subscription-orientated bills.
Conducting a Subscription Audit: Steps to Reveal Hidden Expenses
A subscription audit involves compiling and examining all ongoing subscriptions to assess their necessity, frequency of usage, and cost-effectiveness. This process can uncover forgotten or redundant services and serve as a foundation for cost reduction strategies.
The first step is to gather financial data by reviewing bank statements, credit card bills, and payment platforms like PayPal or Apple Pay. Tools like Truebill (now Rocket Money) or Trim can automate this process by scanning accounts for recurring payments and alerting users about subscription patterns. Manually, compile a list of service names, billing dates, amounts, and renewal terms.
Next, evaluate the usage and value of each subscription. For instance, if you subscribe to a meal kit service but use it only once a month, consider cheaper grocery alternatives. Similarly, if you have multiple streaming platforms, identify which ones you routinely watch and cancel the rest. A practical example involves Jane, a 34-year-old professional who discovered she was paying for five video platforms but only regularly used two. After her audit, she canceled the others, saving $45 monthly.
The audit should also check for duplicated services and evaluate family or group plans that might offer better pricing. Considerations around whether alternative free or cheaper options exist can help identify savings opportunities.
Comparing Subscription Plans: Maximize Value with Informed Choices
Many subscription services provide multiple tiers with varying prices and features. Selecting the optimal plan requires understanding your consumption habits and needs. Comparing these plans side-by-side can highlight hidden costs tied to premium features or unnecessary add-ons.
Below is a comparative table illustrating popular streaming services’ basic versus premium plans as of 2024:
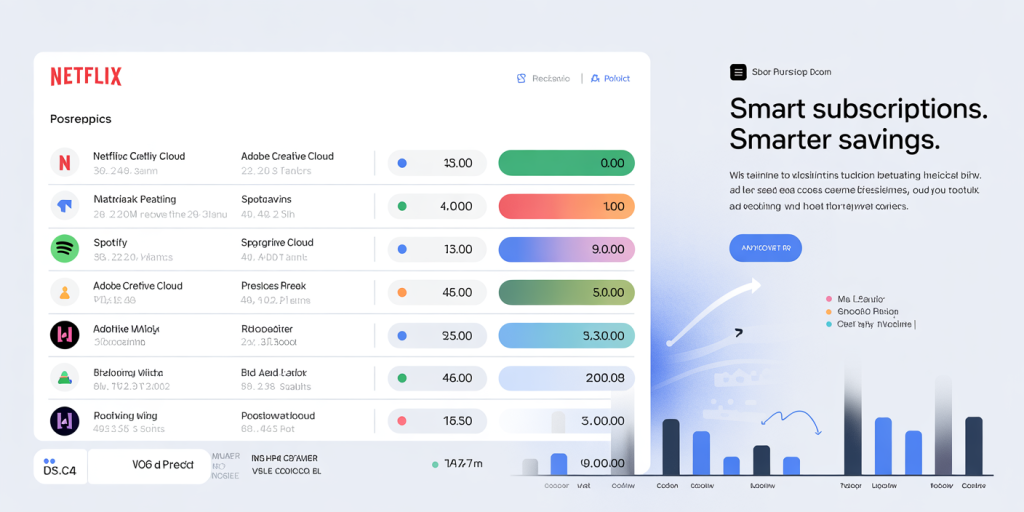
A comparative infographic/table visually contrasting basic vs. premium subscription plans of popular streaming and software services, highlighting key differences, prices, and user profiles to represent “comparing subscription plans” for maximizing value.
| Service | Basic Plan Cost (Monthly) | Premium Plan Cost (Monthly) | Key Differences | Recommended User Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Netflix | $9.99 | $19.99 | SD vs. 4K Ultra HD, 1 vs. 4 screens | Casual viewer (Basic), Family or Content Lovers (Premium) |
| Spotify | $9.99 | $15.99 (Family Plan) | Individual vs. up to 6 accounts | Solo user (Basic), Household or Group (Premium) |
| Adobe Creative Cloud | $20.99 | $52.99 (All Apps) | Single app vs. access to entire suite | Hobbyists (Basic), Professionals (Premium) |
| Disney+ | $7.99 | $13.99 | Ad-supported vs. ad-free, 1 vs. 4 streams | Budget-conscious viewers (Basic), Families (Premium) |
By referencing such comparisons, users can decide whether the additional cost justifies the incremental features. For example, a user who watches Netflix alone might be better off with the basic plan, whereas a family with multiple viewers could benefit from premium to access more simultaneous streams.
Common Pitfalls Leading to Subscription Waste
Several factors contribute to excessive spending on subscriptions, often unknowingly. A common scenario is the automatic renewal trap, where services renew without explicit consent because the user forgets to cancel before the trial ends.
Moreover, psychological factors such as “subscription fatigue” and inertia deter users from reevaluating their subscriptions regularly. The convenience and perceived ongoing value overshadow the actual usage, resulting in paying for services that sit idle. According to a West Monroe study, about 84% of users do not review subscription usage monthly, increasing the likelihood of overspending.
Additionally, businesses’ pricing structures sometimes utilize “decoy pricing” or bundled items with hidden fees. For instance, a fitness app might offer a low monthly fee but upsell nutritional plans or personalized coaching, which significantly inflate costs.
Real-world examples include John, who subscribed to five different software apps for productivity but used only two. Due to confusion about cancellation policies and fear of losing content, he kept all, amassing over $150 in avoidable monthly expenses.
Strategies to Cut Subscription Costs Without Sacrificing Value
Auditing and analyzing your subscriptions enable the development of targeted strategies to optimize spending. One efficient approach is implementing “subscription stacking,” which involves rotating subscriptions based on usage rather than maintaining concurrent memberships.
For example, if you subscribe to multiple streaming platforms, it might make sense to use Netflix for three months, then switch to Disney+ for another three, maximizing entertainment without overlap. This strategy requires understanding service cancellation terms but can yield substantial savings.
Another cost-cutting method is negotiating with providers. Many services offer discounts or promotional rates to retain customers who threaten to cancel. A well-known case occurred in 2023 when a tech-savvy user successfully reduced his gym membership fee by 20% through polite negotiation, citing competitor pricing.
Additionally, group or family plans present significant savings for multiple users. Spotify and Apple Music’s family offerings slash per-person costs compared to individual plans. Monitoring payment methods and consolidating charges through a single credit card or digital wallet can also enhance tracking and control.
Lastly, consider replacing paid services with free alternatives where feasible. For example, using YouTube’s free ad-supported content instead of purchasing multiple video subscriptions or leveraging open-source software instead of costly licensed programs can help reduce expenses.
Future Perspectives: The Evolution of Subscription Management
The subscription economy shows no signs of slowing; its market value is expected to reach $1.5 trillion globally by 2027, according to a report by Grand View Research (2023). However, growing consumer awareness and emerging technologies promise more efficient management of recurring payments.
Artificial intelligence-powered platforms are evolving to provide real-time expenditure tracking, recommendation engines, and even automatic subscription cancellations based on behavioral patterns. Emerging financial apps are introducing “subscription consolidation,” grouping related services while optimizing billing cycles to prevent overlapping charges.
A futuristic digital dashboard powered by AI displaying real-time subscription expenditure tracking, automatic alerts, and cancellation options, symbolizing the “future of subscription management” with emerging technologies and consumer empowerment.
On the regulatory front, policymakers are focusing on greater transparency and simplified cancellation processes. For instance, the European Union’s Digital Services Act includes provisions to make subscription terms clearer and easier to terminate. This trend may inspire similar legislation worldwide, empowering consumers against hidden costs.
Moreover, industry innovations such as “pay-as-you-use” subscriptions that charge based on actual consumption instead of flat fees could revolutionize service billing models, making payments fairer and more aligned with individual use.
For consumers, staying informed, regularly auditing subscriptions, and leveraging technological tools will remain essential practices in personal finance management as these trends unfold.



Post Comment