Complete Guide to Life Insurance: Types, Benefits, and Choosing the Right Policy
Anúncios
Life insurance is a crucial financial tool that protects your loved ones and secures your family’s future in the event of unexpected tragedies. Despite its importance, many people remain uninformed about the types of life insurance available, their specific benefits, and how to choose the best policy based on personal circumstances. According to the 2023 Insurance Barometer Study by LIMRA, nearly 39% of Americans do not have life insurance, leaving families vulnerable to financial instability after the loss of a breadwinner.
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify life insurance, providing detailed insights into the different policy types, the benefits attached to each, and practical criteria for selecting the policy that fits your needs. Drawing examples from real-life cases and current market data, this article equips readers with the knowledge necessary to make confident decisions about their life insurance.
Understanding Life Insurance: What It Is and Why It Matters
Anúncios
Life insurance is a contract between the policyholder and an insurer where the insurer promises to pay a designated beneficiary a sum of money upon the death of the insured person. This financial security can cover debts, funeral costs, and provide income replacement for dependents. For example, a family that loses its primary earner can use life insurance benefits to maintain their lifestyle, pay off mortgages, or fund children’s education.
One notable case is the story of Jennifer, a single mother living in Texas who purchased a term life policy at age 35 for $500,000. When Jennifer unexpectedly passed away due to a car accident three years later, her policy ensured that her two children could stay in their home and attend college without financial hardship. This case underscores how life insurance is more than just a financial instrument—it’s a safety net that offers peace of mind to families facing challenging realities.
Anúncios
Types of Life Insurance Policies
Life insurance comes in various types; the most common are Term Life Insurance, Whole Life Insurance, Universal Life Insurance, and Variable Life Insurance. These policies differ mainly in cost, coverage duration, investment components, and flexibility.
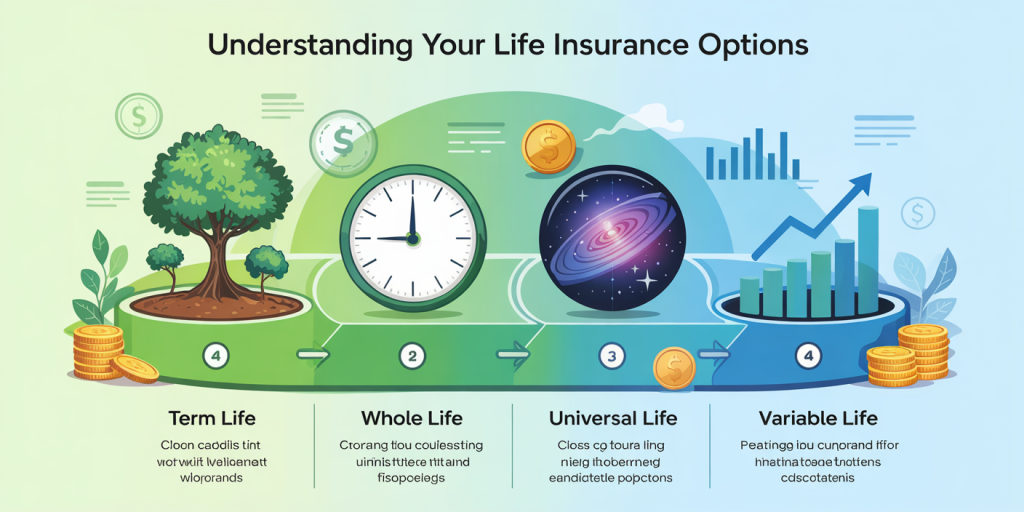
1. Term Life Insurance
Term life insurance provides coverage for a specified period, typically 10, 20, or 30 years. If the insured dies during this term, the beneficiary receives the death benefit. This option is usually the most affordable because it does not have a cash value component. Term life is ideal for those seeking maximum coverage during critical years, such as while raising children or paying off debts.
For instance, David, a 40-year-old father of two, purchased a 20-year $1 million term policy to protect his family until his children graduate college. His annual premium is relatively low—about $500—compared to permanent insurance alternatives.
2. Whole Life Insurance
Whole life insurance offers lifetime coverage as long as premiums are paid. Besides providing a death benefit, it accumulates cash value on a tax-deferred basis, which policyholders can borrow against or withdraw. This policy is more expensive than term insurance because of its extra benefits and guaranteed level premiums.
Maria, a 50-year-old entrepreneur, chose whole life insurance to combine protection with forced savings. Over 15 years, her policy’s cash value has grown to over $75,000, which she used as collateral for a business expansion loan.
3. Universal Life Insurance
Universal life insurance provides more flexibility than whole life policies. It allows policyholders to adjust their premiums and death benefits within certain limits. This policy also builds cash value, with interest credited based on prevailing market rates.
An example is Tom, who started with a $300,000 universal life policy when he was 45. When his income rose, he increased both his death benefit and premium contribution, leveraging the flexible features. This adaptability makes universal life attractive for those whose finances fluctuate over time.
4. Variable Life Insurance
Variable life combines life insurance with investment options, letting policyholders allocate cash value among various subaccounts similar to mutual funds. While this can lead to higher returns, it also carries investment risk. These policies are suitable for those with a strong appetite for risk and investment knowledge.
Jessica, an investor in her 30s, used a variable life policy as part of her estate planning. Though she accepted market volatility, she benefitted when markets performed well, increasing her cash value substantially.
Comparative Table of Life Insurance Types
| Policy Type | Coverage Duration | Premium Cost | Cash Value Growth | Flexibility | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Term Life | Fixed (10-30 years) | Low | None | Low | Short-term needs, budget-conscious |
| Whole Life | Lifetime | High | Guaranteed | Low | Long-term coverage, cash value accumulation |
| Universal Life | Lifetime | Moderate to High | Varies | High | Flexible premiums, investment potential |
| Variable Life | Lifetime | High | Market-based | Moderate | Risk-tolerant, investment-savvy individuals |
Key Benefits of Life Insurance
Life insurance offers multiple benefits beyond the fundamental death benefit. These advantages play a crucial role in overall financial planning.
Firstly, life insurance provides income replacement. A 2022 study by the National Association of Insurance Commissioners found the average American family would need a death benefit between 7 and 10 times the primary earner’s annual salary to maintain their lifestyle. For example, if a person earns $50,000 annually, they may need at least $350,000 to $500,000 in coverage to replace lost income adequately.
Secondly, life insurance can pay off debts and final expenses, including mortgages, credit cards, and medical bills. This prevents surviving family members from being burdened financially. The case of Mark, who passed away leaving a $200,000 mortgage, demonstrates this—it was his $300,000 life insurance payout that allowed his spouse to retain their home without financial strain.

Additionally, some policies accumulate cash value, which can serve as a source of emergency funds or supplemental retirement income. This dual function acts as a forced savings mechanism.
Tax advantages also make life insurance appealing. Death benefits are typically income tax-free for beneficiaries, and cash value growth is tax-deferred. These features can enhance estate planning efforts.
How to Choose the Right Life Insurance Policy
Choosing the appropriate life insurance policy depends on several personal factors, including financial goals, family needs, budget, and risk tolerance. Conducting a thorough needs assessment is vital in selecting the right plan.
Start by evaluating your financial responsibilities: debts, dependents, future expenses like college tuition, and income replacement needs. Term life is often sufficient for a young family with limited budget but high financial obligations. On the other hand, individuals seeking lifetime coverage with investment components may prefer whole or universal life policies.
Next, consider your budget, as premiums vary significantly among policy types. For example, a $500,000 20-year term life insurance policy may cost $400 annually for a healthy 30-year-old, whereas a comparable whole life policy could exceed $3,000 annually.
Another important factor is the policy’s flexibility and portability. If your circumstances might change—such as switching jobs or income fluctuations—universal life policies offer adaptability in premium payments and death benefits.
It’s wise to consult with a licensed insurance agent or financial advisor to analyze your specific situation. They can provide personalized recommendations and guide you through underwriting, which considers health, lifestyle, and other risk factors affecting premiums.
Practical Examples of Life Insurance in Action
To illustrate the importance of life insurance, consider the story of the Harris family. James, the family’s primary earner, passed away suddenly at age 45. Fortunately, he had a $1 million term life insurance policy. The benefit helped the family cover immediate expenses, including funeral costs of $15,000, clear a $250,000 mortgage, and replace lost income while his spouse, Linda, retrained for a new job. Without insurance, the family would have faced significant financial strain and risked losing their home.
In contrast, Cynthia, a single professional with minimal financial dependents, opted for a whole life policy at age 30. Over ten years, her policy accrued a $50,000 cash value she leveraged as a down payment on a condo. This use of insurance demonstrates its role beyond just death protection, offering financial flexibility during life.
Emerging Trends and Future Perspectives in Life Insurance
The life insurance industry is evolving rapidly, embracing technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. One notable trend is the rise of digital life insurance platforms and insurtech companies that offer streamlined application processes and instant underwriting through AI-enabled tools. This innovation reduces barriers to entry and enables more people to access coverage quickly.
Another development is the increasing popularity of customizable policies that blend traditional life insurance with riders for critical illness, disability, or long-term care coverage. Consumers now seek comprehensive solutions that adapt to complex and shifting healthcare landscapes.
Data also indicates a growing awareness among younger demographics, particularly millennials, who are prioritizing financial security despite historically lower life insurance ownership. According to a 2023 survey by Policygenius, 56% of millennials expressed interest in purchasing life insurance within the next five years, driven by life milestones such as marriage and parenthood.
Looking ahead, sustainability and social responsibility are influencing insurer practices. Many companies are integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into their investment portfolios and underwriting guidelines, appealing to conscious consumers.
Moreover, the synergy between genomics and life insurance underwriting could refine risk assessment accuracy. While ethical challenges exist, these advances may lower premiums for individuals in good health and facilitate fairer pricing structures.
Overall, life insurance is poised to become more accessible, flexible, and integrated into broader financial planning frameworks, empowering more families worldwide to secure peace of mind.
This comprehensive guide, spanning the types, benefits, and decision-making processes surrounding life insurance, underscores its indispensable role in personal finance strategies. In an uncertain world, taking proactive steps to evaluate and obtain the right policy can offer invaluable protection and financial confidence for every stage of life.


Post Comment