Understanding and Avoiding the Debt Trap: Financial Strategies for Millennials
Anúncios
The financial landscape today is vastly different from previous generations, particularly for millennials—those born roughly between 1981 and 1996. This generation faces unique challenges like soaring student loan debt, a fluctuating job market, and rising living costs, all contributing to increased financial vulnerability. With personal debt levels ballooning, understanding how to navigate financial decisions and avoid the debt trap has become essential for millennials aiming for long-term economic stability.
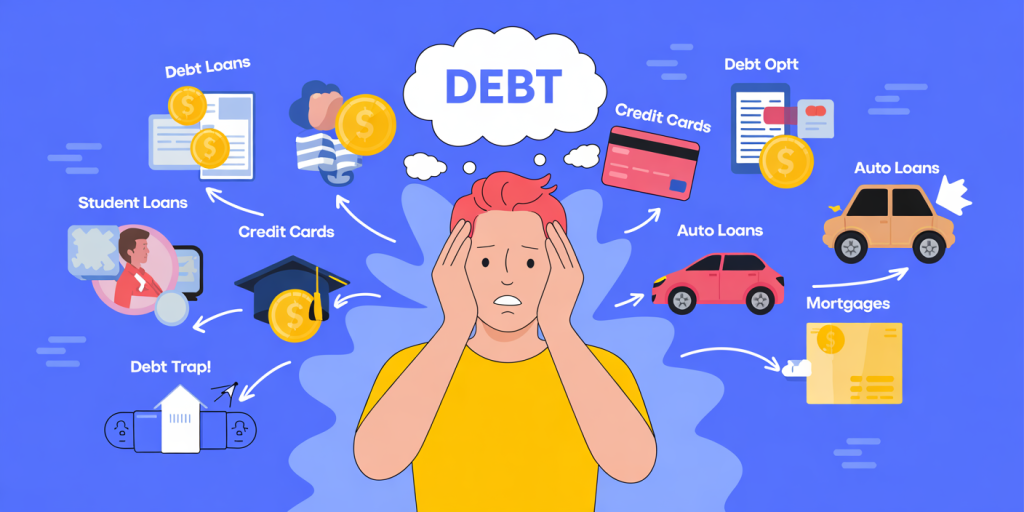
Millennials carry the highest levels of debt compared to previous generations at the same age. According to a 2023 report by Experian, the average millennial carries around $90,460 in debt, including student loans, credit card debt, auto loans, and mortgages. Understanding where this debt comes from and adopting practical strategies can help young adults avoid deep financial pitfalls and achieve financial health.


Anúncios
The Debt Trap: Causes and Consequences
The “debt trap” describes a scenario in which individuals accumulate increasing debt due to high-interest rates, insufficient repayments, and constant borrowing to cover everyday expenses. Millennials often fall into this trap because of multiple factors—rising education expenses, stagnant wages, and economic disruptions such as recessions and pandemics.
Anúncios
One major contributor is student loans, which for many millennials have become a crushing burden. The Federal Reserve notes student loan debt surpassed $1.8 trillion in 2023, with millennials responsible for the majority. When high loan repayments coincide with credit card balances and other debts, the monthly financial load can become overwhelming. For example, Sarah, a 29-year-old marketing professional, has $50,000 in student loans and regularly carries $4,000 in credit card debt. The minimum payments on her debts consume a third of her monthly income, preventing her from saving or investing.
Financial consequences of being caught in a debt trap include poor credit scores, reduced borrowing ability, mental health stress, and delayed milestones like buying a home or starting a business. The cycle perpetuates itself as borrowers resort to high-interest loans or payday financing to meet urgent needs, worsening their financial status over time.
Common Types of Debt Burdening Millennials
Understanding the types of debt common among millennials is crucial to developing effective strategies for avoidance and management. Below is a comparative overview of key debt categories, their average amounts, and their impact on millennials’ finances.
| Debt Type | Average Debt per Millennial (2023) | Typical Interest Rate | Impact on Financial Health |
|---|---|---|---|
| Student Loans | $38,000 | 4.5% – 7% | Long-term liability; affects credit scores |
| Credit Cards | $4,200 | 15% – 25% | High-interest; difficult to pay off quickly |
| Auto Loans | $18,500 | 4% – 7% | Moderate impact; essential for mobility |
| Mortgages | $150,000 (younger millennials) | 3% – 5% | Long-term asset; debt but often equity-building |
Student loans represent the highest average burden, with many millennials dedicating years to repayment. Credit card debt, while smaller in amount, accumulates rapidly due to higher interest rates, often leading to spiraling balances. Auto loans and mortgages are often viewed as “good debt,” as they typically fund assets, but mismanagement can still cause financial strain.
For example, James, a 32-year-old software engineer, strategically prioritizes paying off his credit card balance monthly to avoid interest but deliberately carries his low-interest student loan due to its comparatively benign impact on his cash flow and credit score. This approach exemplifies how understanding debt types affects repayment decisions.
Practical Financial Strategies to Escape the Debt Cycle
To overcome or avoid the debt trap, millennials need actionable and realistic financial strategies. These methods focus on budgeting, debt prioritization, and smart borrowing.
1. Develop a Detailed Budget and Track Spending Creating a budget is foundational to managing personal finances. Many millennials tend to underestimate their daily expenditures, which can lead to uncontrolled spending and debt accumulation. Utilizing digital tools such as Mint or YNAB (You Need A Budget) can help monitor expenses and identify savings opportunities.
For instance, Jane noticed her discretionary spending on dining out was significantly higher than planned. By reallocating $150 monthly from her dining budget to a debt repayment fund, she accelerated her credit card payoff schedule by six months.
2. Snowball and Avalanche Methods for Debt Repayment There are two established debt repayment techniques well-suited for millennials: *Snowball Method*: Pay off the smallest debt first to gain momentum and motivation. *Avalanche Method*: Prioritize debts with the highest interest rates to minimize total interest paid.
Choosing between the two depends on individuals’ psychological preference for quick wins versus cost-saving strategies. John, with multiple credit cards, followed the avalanche method by targeting the card with a 22% interest rate first, saving him nearly $1,200 in interest over two years compared to the snowball approach.
3. Avoid New Debt and Use Credit Wisely Controlling the use of credit cards and borrowing only when absolutely necessary can prevent debt escalation. Millennials should also be aware of predatory lending practices, such as payday loans or high-interest buy-now-pay-later plans.
Building and maintaining good credit scores through timely payments not only allows access to better loan terms but also reduces overall borrowing costs. According to FICO, a credit score above 700 can reduce mortgage interest rates by up to 0.5%, saving thousands over a loan term.
The Role of Financial Education and Employer Support
Financial literacy remains a significant barrier to effective debt management among millennials. Surveys by the National Endowment for Financial Education (NEFE) reveal that nearly 60% of young adults feel “not confident” managing their finances, highlighting the urgent need for accessible education.
Employers have started stepping in, offering financial wellness programs that provide practical training on budgeting, investing, and debt management. Companies like PwC and Starbucks have integrated such programs into employee benefits, resulting in improved productivity and reduced stress.
Programs typically include workshops on student loan repayment options, emergency savings, and retirement planning. Offering direct advice paired with tools like employer-matched savings schemes encourages millennials to think holistically about their finances beyond just debt repayment.
Technology and Tools to Facilitate Smart Money Management
The surge in fintech innovation has given millennials a diverse set of tools to take control of their finances and avoid debt pitfalls. Mobile apps for budgeting, investing, and automated savings are a few examples transforming personal finance management.
Consider the popularity of apps like Acorns, which rounds up purchases and invests spare change, or Digit, which analyzes spending patterns to automate savings toward financial goals. These tools lower the barrier to entry for investing and saving, helping millennials build financial resilience.
Tech-driven lending platforms also provide more transparent and competitive loan options compared to traditional banks, often featuring lower interest rates and flexible repayment schedules suitable for younger borrowers.
Looking Ahead: Financial Empowerment and Debt-Free Futures
Millennials’ financial landscape will continue evolving, driven by changes in technology, economic conditions, and societal attitudes toward credit and debt. As the generation ages, many will move toward homeownership, family planning, and wealth-building activities requiring strong financial fundamentals.
Policy changes such as student loan forgiveness programs and increased regulation of payday lenders could ease some pressures, but ultimately, personal financial empowerment remains key. Millennials equipped with sound budgeting habits, clear repayment plans, and a proactive approach to credit use are better positioned to break free from the cycle of debt.
Moreover, the integration of financial wellness into education systems and workplaces promises broader financial competence across the generation. The future indicates a shift from reactive debt management to proactive financial planning, allowing millennials to achieve economic security and intergenerational wealth transfer.

By understanding the unique causes of modern debt traps and implementing tailored financial strategies, millennials can navigate the complexities of their economic environment. With disciplined budgeting, strategic repayment, and leveraging technology and education, it is possible to avoid the pitfalls of debt and build a stable, prosperous future.


Post Comment